This article is the first part of a series of articles exploring the critical components of developing effective training simulators.
After the release of Inscape VTS 10 and the integration of Unreal Engine as its new graphics engine, Inscape VTS Product Manager Eric Menou reflects on the perceived central role of the 3D engine in a training simulator. Contrary to popular belief, he explains why choosing a specialized tool is crucial for successfully developing a training system.
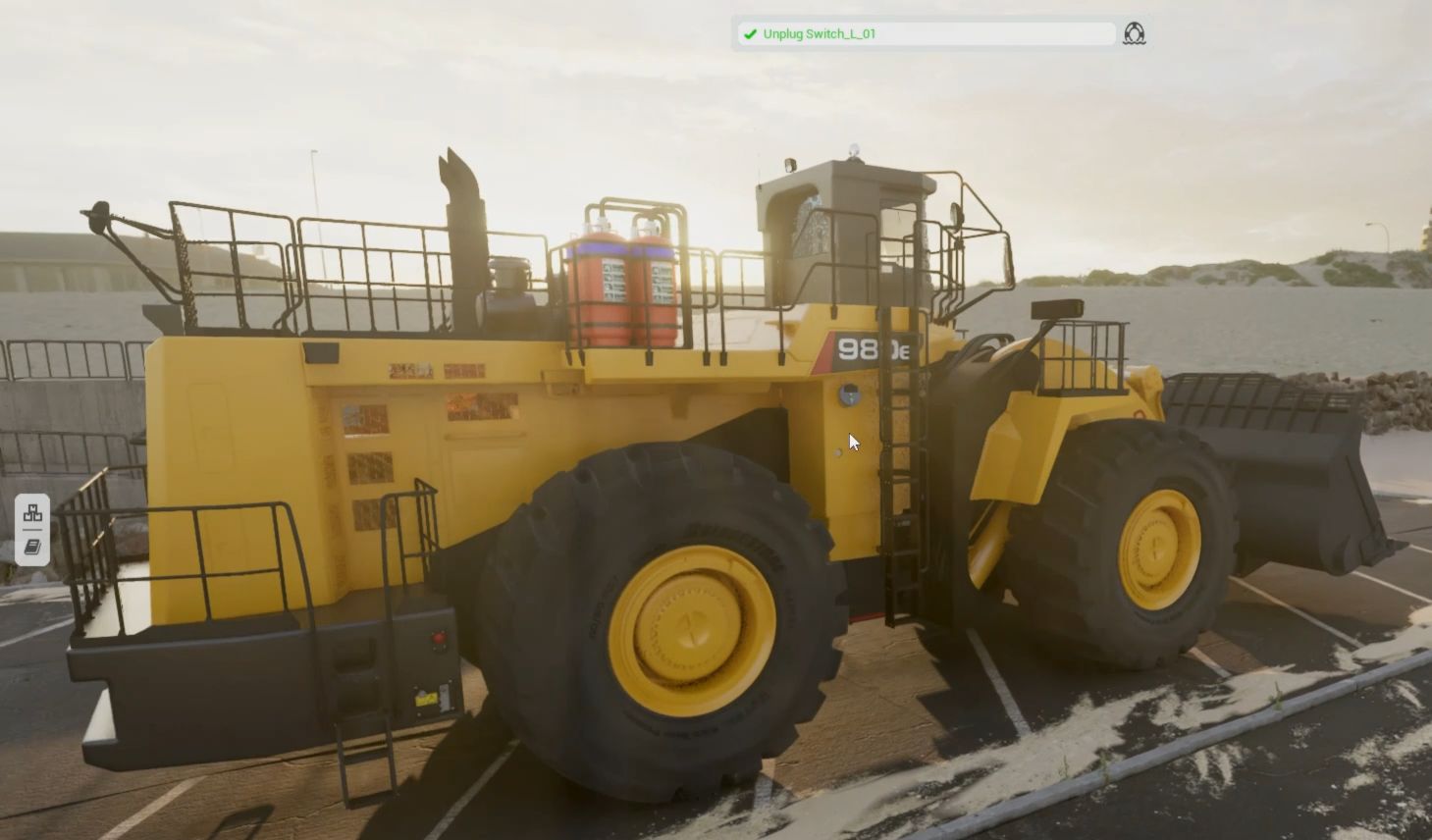
Over the years, I've occasionally encountered the notion that the 3D engine is a decisive factor in the development of a training simulator, likely because it's usually the first feature that catches the eye. One might even get the impression that modern tools like Unity 3D or Unreal Engine, with all their functionalities, could suffice to develop a complete training system. The fact is, they allow for the rapid creation of a functional prototype showcasing an attractive 3D environment coupled with some interactions and animations. However, unless one limits themselves to developing a proof of concept, these modern platforms derived from video games fall far short of addressing all the challenges involved in developing a simulator. While visual realism greatly contributes to the adoption of a trainer or virtual simulator, the graphical component is neither the most significant in development costs nor the most critical in achieving educational objectives. Moreover, despite all the features and tools that 3D engines offer in terms of graphical realism, data processing, and graphical programming, and despite efforts to make them easier to use, they remain development tools intended for coders and are particularly oriented towards video game development.
To support the digitization of training and ensure these tools can be widely adopted, it is essential to have platforms that enable subject-matter experts to produce standardized content on a large scale, which is easy to evolve and can be leveraged in multiple ways. This is a necessary step to reduce the development costs of virtual training content and increase its usage, whether for large state programs or within smaller organizations.
Bridging the gap between theory and practice
Virtual Trainers and Simulators: Transforming training for the future
Trainers and simulators are essential tools in modern training methodologies, designed to replicate real-world scenarios for educational purposes. A trainer is typically a system or device that provides hands-on practice and instruction in a specific skill or task. On the other hand, a simulator is a more comprehensive system that replicates the conditions and environment of a real-world process or operation, allowing users to practice and hone their skills in a controlled, risk-free setting. In Inscape VTS, these two aspects are addressed through non-linear scenario editing tools and simulation graphs, both of which can coexist to meet educational needs at the most reasonable cost.
These tools can be purely virtual, physical, or a hybrid of both. Virtual trainers and simulators use computer-generated environments to create realistic training scenarios. Physical trainers and simulators involve tangible equipment and devices that mimic real-world tools and machinery. Hybrid systems combine both virtual and physical elements, offering a more immersive and comprehensive training experience.

The primary commonality between trainers and simulators is the concept of "learning by doing." This hands-on approach allows trainees to engage actively with the training material, leading to better retention and understanding of the skills being taught. Some typical fields of use for these tools include:
- Virtual Maintenance Trainer (VMT): These simulators are designed to train individuals in the maintenance and repair of complex machinery and equipment. They provide a safe and cost-effective way to practice maintenance tasks without the risk of damaging expensive equipment.
- Operations Training: Simulators in this field are used to train personnel in the operation of various systems and processes, such as manufacturing lines, power plants, and other industrial operations. They help trainees understand the intricacies of the systems they will be working with and prepare them for real-world challenges.
- Pilot Training: Flight simulators are a well-known example of this category. They provide aspiring pilots with a realistic and immersive environment to practice flying, navigation, and emergency procedures without the risks associated with actual flight.
Overcoming the challenges of content creation
One of the most significant challenges in developing trainers and simulators is creating accurate and effective training content. This process often involves translating complex documentation and domain expertise into interactive and engaging training scenarios. Subject-matter experts play a crucial role in this process, as their knowledge and experience are essential for ensuring the training material is both accurate and relevant. Creating high-quality training content requires a deep understanding of the subject matter, as well as the ability to design interactive and immersive training experiences.
This is where specialized tools like Inscape VTS come into play. By providing a no-code authoring platform, Inscape VTS enables subject-matter experts to create and update training content without the need for extensive programming knowledge. This approach not only reduces development costs but also ensures that the training material remains up-to-date and relevant to the trainees' needs.


